Africa is stepping into the spotlight with a groundbreaking initiative that could reshape the dynamics of global carbon markets. The Africa Carbon Support Facility (ACSF) has been unveiled as a pivotal strategy to position the continent as a frontrunner in climate finance and sustainability efforts.
The launch of ACSF at the African Development Bank Group’s 2025 Annual Meetings in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire signifies Africa’s determination to leverage its natural resources and address pressing environmental challenges. This strategic move aims to catalyze significant investments by streamlining and mitigating risks associated with carbon trading across Africa.
“The Africa Carbon Support Facility is a game-changer in our quest for sustainable development. It not only attracts investments but also fosters an inclusive and robust carbon market ecosystem that benefits African nations directly,”
remarked a key official involved in the initiative.
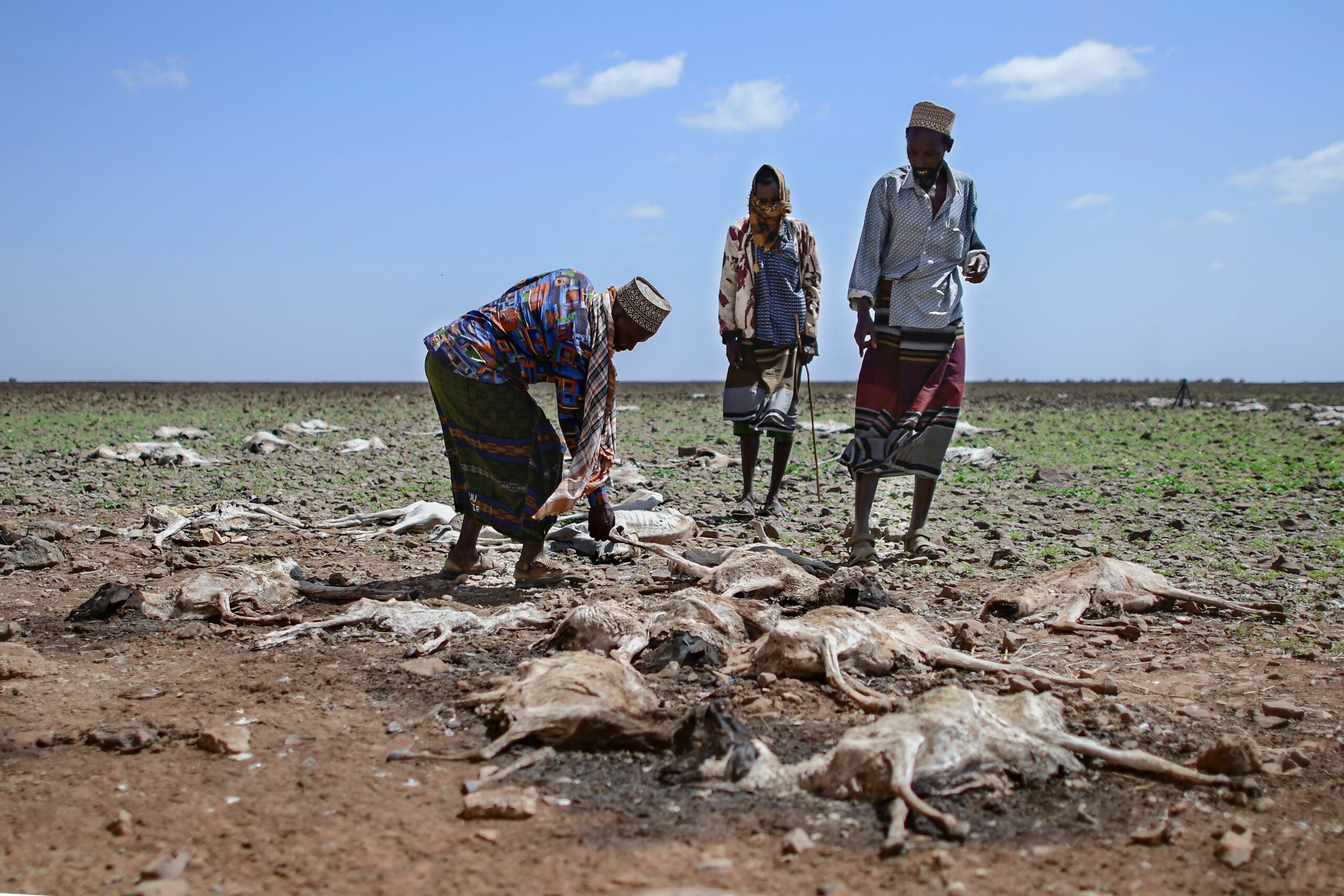
In light of escalating climate change impacts on the continent, such as droughts, sea-level rise, and erratic weather patterns, Africa recognizes the urgent need to take proactive measures. Despite contributing minimally to global greenhouse gas emissions, African countries are disproportionately affected by environmental crises. The ACSF emerges as a beacon of hope in this challenging landscape.
Designed around five core pillars, the ACSF sets out to de-risk carbon credit supply, boost buyer demand, enhance market infrastructure, improve policy frameworks, and mobilize private capital effectively. These pillars are strategically crafted to dismantle long-standing barriers obstructing Africa’s full participation in international carbon markets.
Explaining these pillars further, an industry expert noted,
“De-risking carbon credit supply involves supporting local project developers by providing technical assistance and financial guarantees. This empowers smaller players to engage meaningfully in what was previously perceived as an exclusive domain.”
Moreover, stimulating buyer demand for African carbon credits is crucial for expanding market opportunities and ensuring credibility within global trading systems. By focusing on infrastructure development and policy alignment with national climate goals, the ACSF aims to fortify Africa’s foundation for sustainable growth through climate financing mechanisms.
One of the critical hurdles addressed by ACSF is investor reluctance due to perceived risks associated with African markets. The facility introduces innovative risk-sharing mechanisms like credit guarantees and blended finance models tailored to attract more investors across diverse sectors such as renewable energy, forestry, agriculture, and waste management.
The emphasis on equity stands out as a defining feature of Africa’s approach towards carbon trading. By prioritizing fair revenue distribution among local communities engaged in conservation activities or emissions reduction initiatives like reforestation projects—carbon markets become instruments for fostering inclusive development while preserving natural resources sustainably.
A notable aspect highlighted during discussions surrounding African carbon markets is data integrity. Ensuring transparent measurement methodologies alongside robust reporting systems plays a pivotal role in enhancing credibility within international standards—a prerequisite for securing investor confidence and bolstering market participation from indigenous stakeholders.
As Africa embarks on this transformative journey towards becoming a prominent player in global climate solutions through its proactive stance on carbon markets—the continent underscores its potential impact not only on regional development but also on shaping broader narratives around sustainability worldwide.
With ambitious goals set forth by ACSF signaling Africa’s readiness to lead rather than follow—collaboration among various stakeholders becomes paramount for translating vision into tangible outcomes that benefit both ecosystems and economies alike. The momentum generated by this strategic shift has profound implications not just for Africa but potentially serves as an inspiration for other developing regions seeking resilient pathways amidst climatic uncertainties.








Leave feedback about this